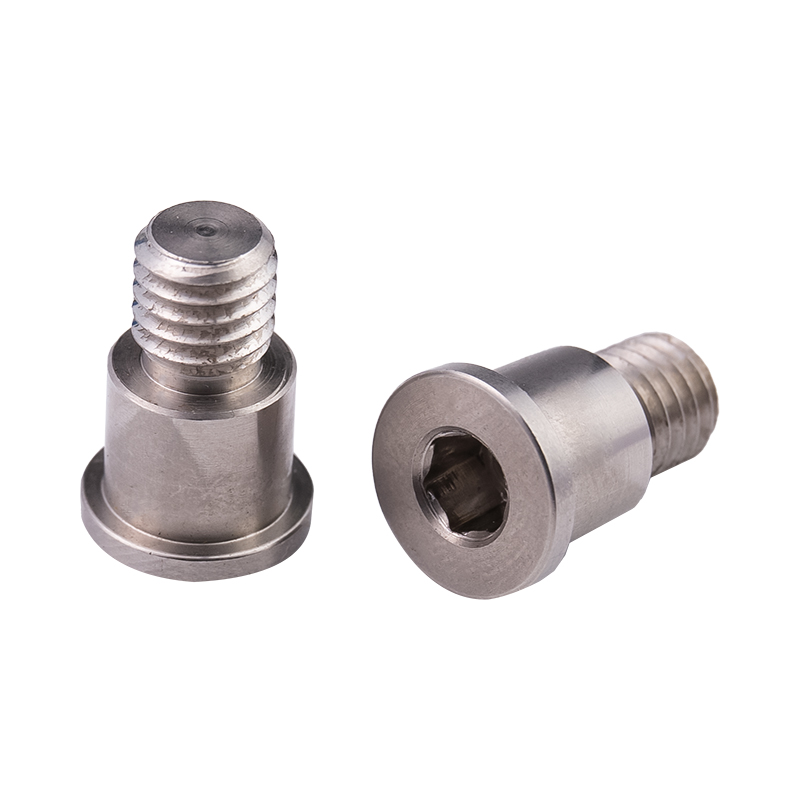
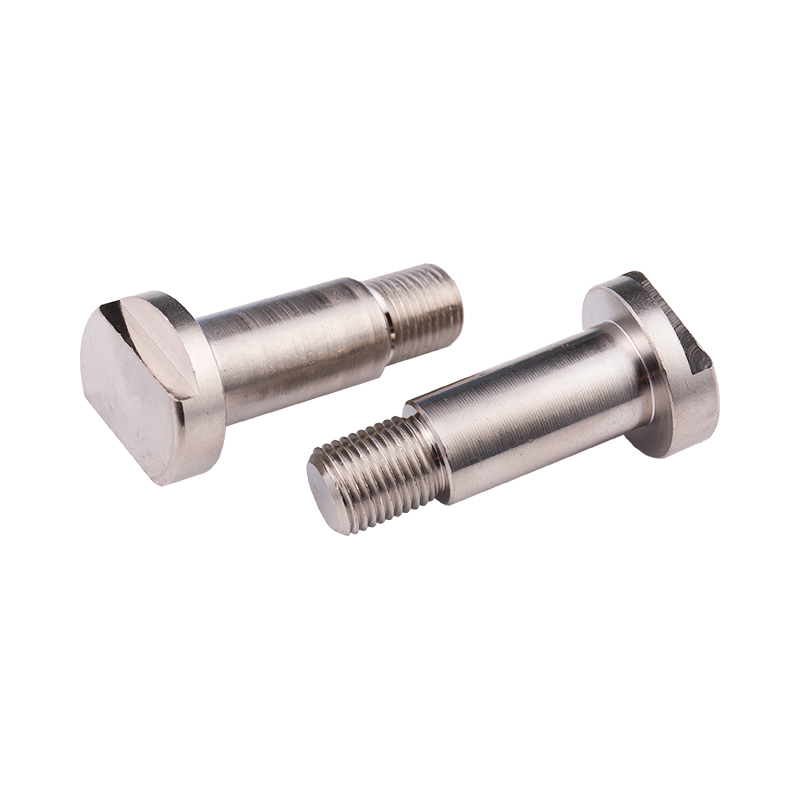
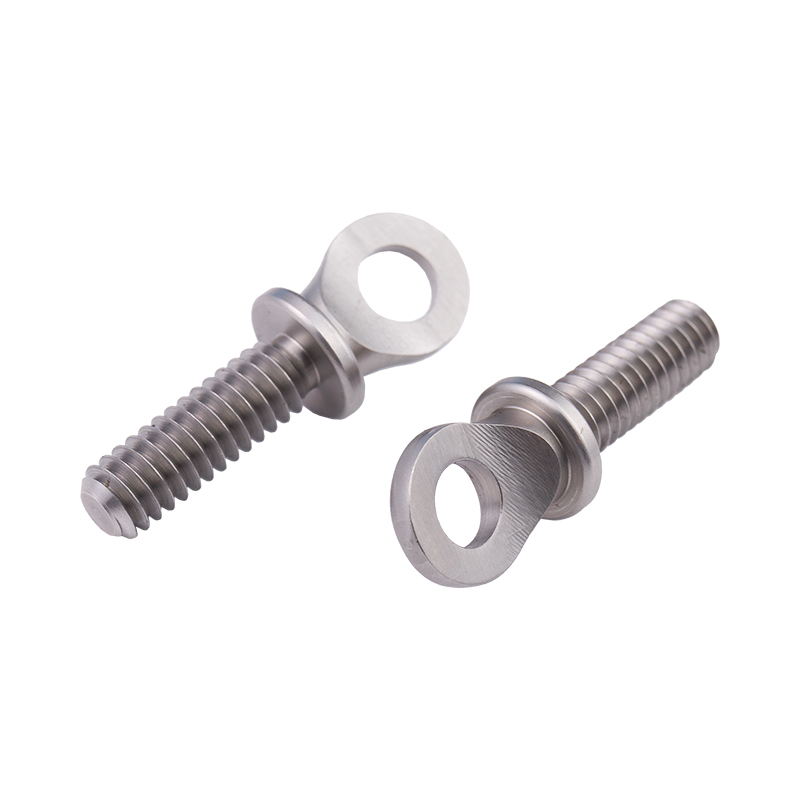
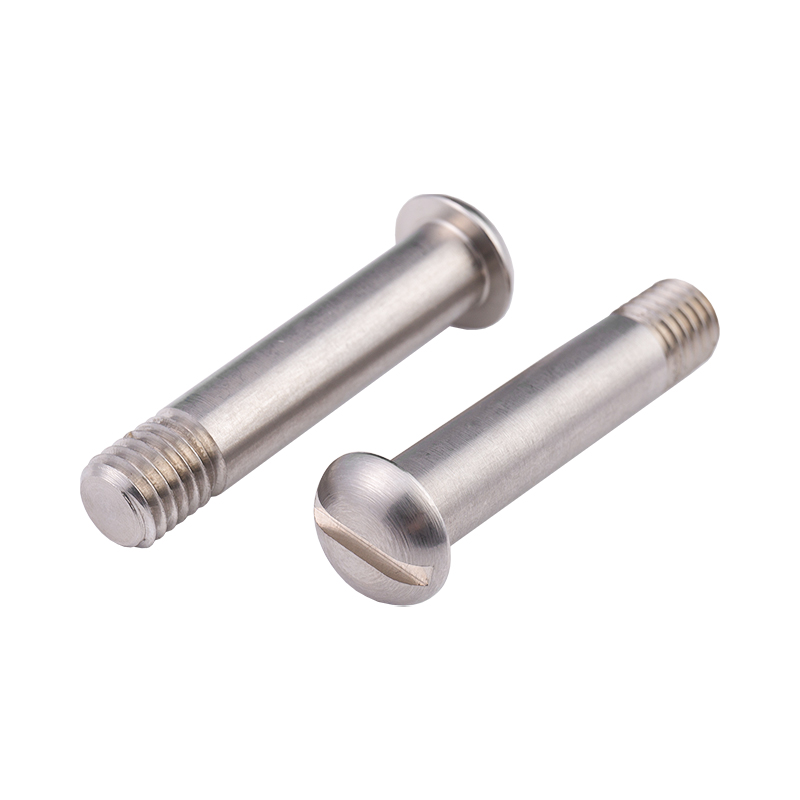
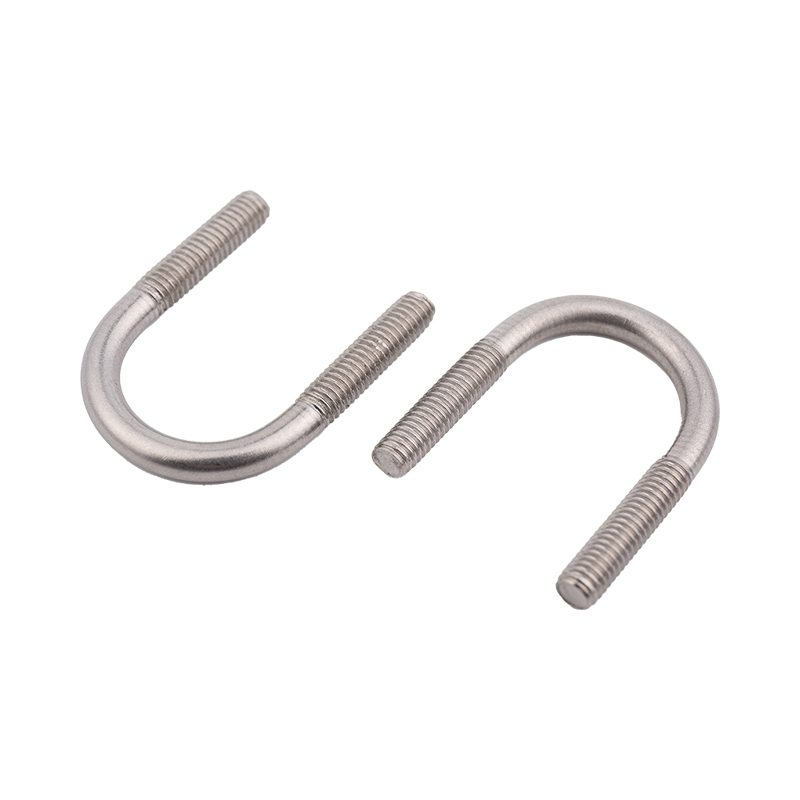
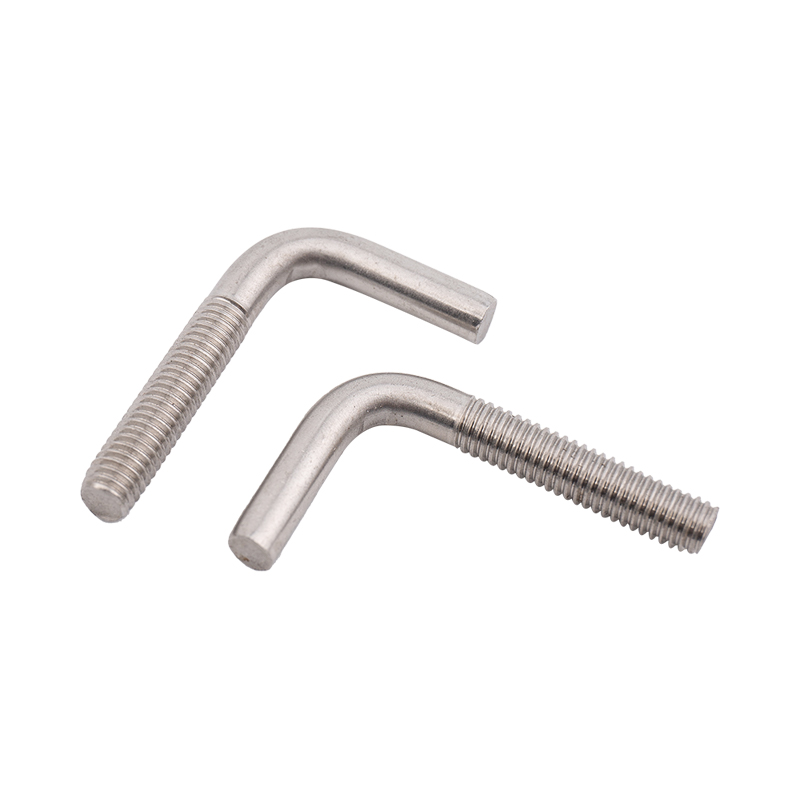
Definition and Basic Concept of Hexagonal Rivet Nuts Hexagonal rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to create strong, load-bearing threads in thin or hollow materials where convention...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Understanding Sealing Requirements in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Hydraulic and pneumatic connections operate under internal pressure, media flow, and frequent pressure fluctuations. In these syst...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Screw Hardware Screw hardware is a fundamental component in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. It plays a critical role in joining materials securely, providing structural ...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Round Head Cross Bolts Round head cross bolts are a type of fastener widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. They feature a rounded head with a cross slot ...
READ MORE
What are the specific modifications that can be made to non-standard stainless steel bolts?
Several modifications can be made to non-standard stainless steel bolts to tailor them to specific applications. Some of these modifications include:
Dimensional Changes:Adjusting the length, diameter, or thread pitch to meet specific size requirements.
Customizing the head style (e.g., hexagon, socket, or round) and dimensions.
Material Composition:Using different grades of stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316, or 17-4 PH) based on environmental conditions or desired properties such as corrosion resistance or strength.
Adding alloying elements to enhance specific properties like hardness or temperature resistance.
Surface Finishes:Applying coatings or treatments for improved corrosion resistance, such as passivation, electroplating, or coating with materials like zinc or nickel.
Polishing or grinding the surface for aesthetic purposes or to achieve specific surface roughness requirements.
Thread Configurations:Modifying the thread profile (e.g., standard, fine, or coarse threads) to optimize engagement or torque resistance.
Head and Drive Styles:Designing specialized heads for unique tooling requirements or aesthetic considerations.
Incorporating different drive types (e.g., Phillips, slotted, or Torx) based on installation needs or security requirements.
Special Features:Adding features like serrations, grooves, or locking mechanisms to prevent loosening under vibration or dynamic loads.
Integrating sealing elements or washers for enhanced sealing or pressure resistance.
Can these bolts withstand high levels of vibration or stress without loosening?
Non-standard stainless steel bolts can be engineered to withstand high levels of vibration or stress without loosening through various design features and modifications.
Bolts can be designed with specialized thread locking features such as serrations, deformable threads, or mechanical locking devices. These mechanisms create additional friction between the bolt and the mating threads, reducing the likelihood of loosening due to vibration.
Properly applied preload or tension on the bolt during installation helps maintain clamping force, even in the presence of vibration. Techniques such as torque tightening or applying a specific preload using calibrated tools ensure that the bolt remains securely fastened.
Coatings or adhesives with anti-vibration properties can be applied to the threads or mating surfaces to increase friction and prevent self-loosening. These coatings may include thread-locking compounds, adhesives, or polymer coatings.
Bolts with unique thread profiles, such as asymmetrical threads or multi-start threads, can enhance resistance to loosening by distributing the load more evenly along the length of the thread engagement.
In addition to the primary fastening mechanism, secondary locking features like nylon inserts, prevailing torque nuts, or cotter pins can be incorporated to provide extra security against loosening.



 русский
русский Español
Español