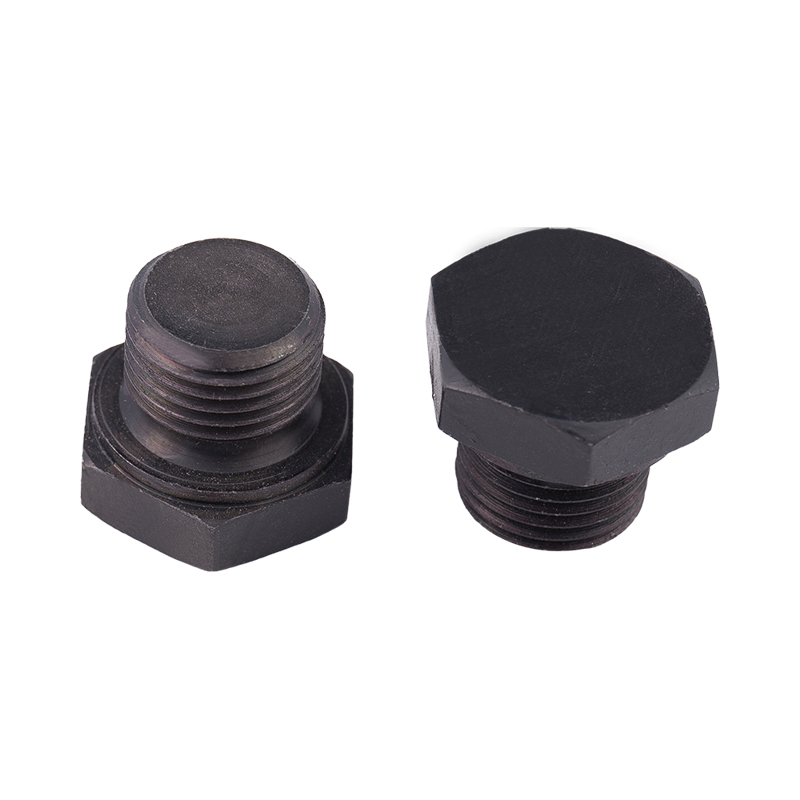
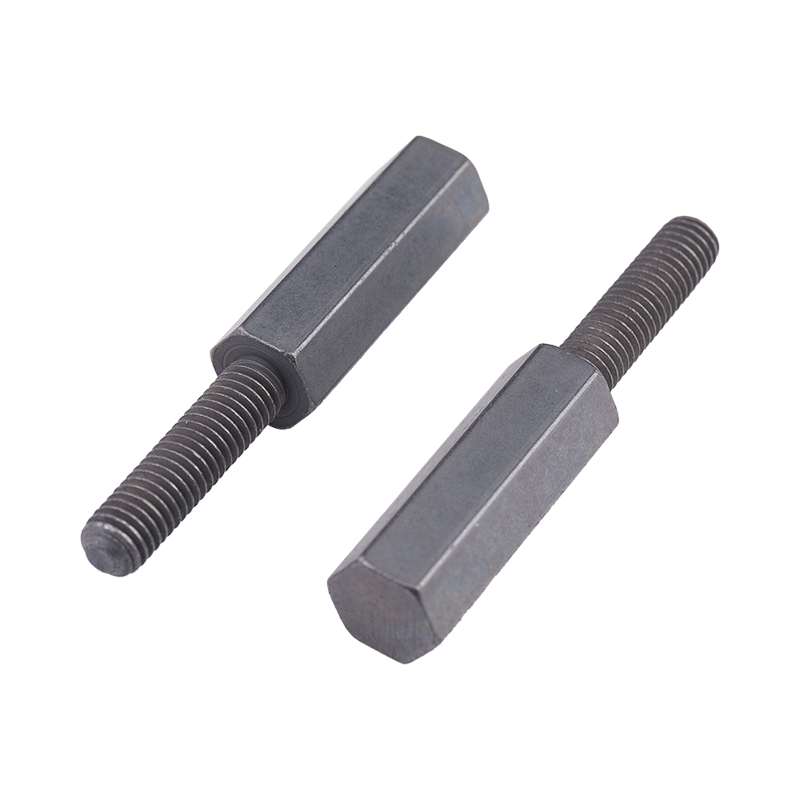
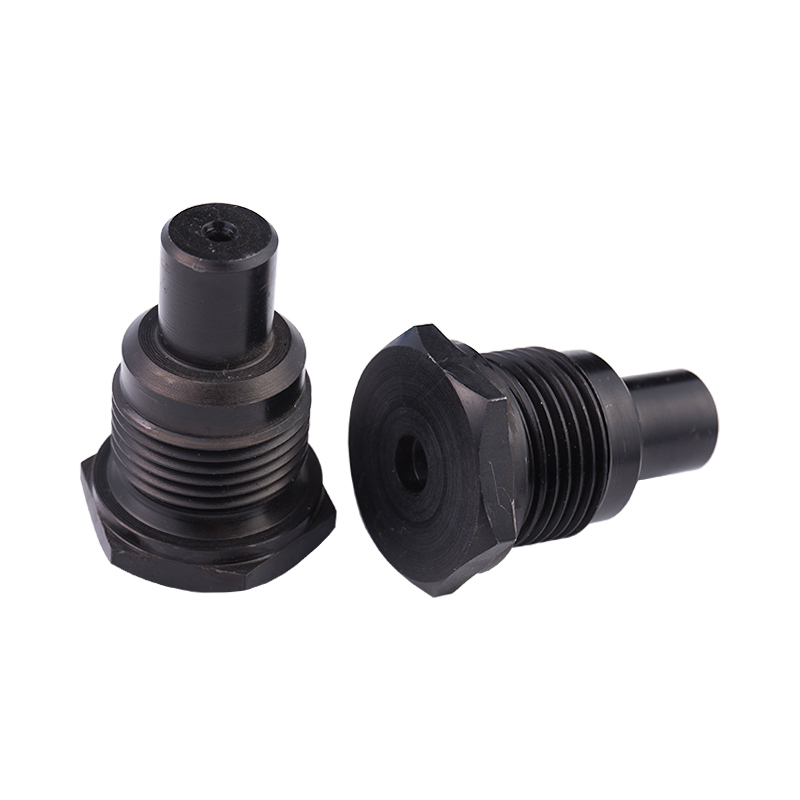
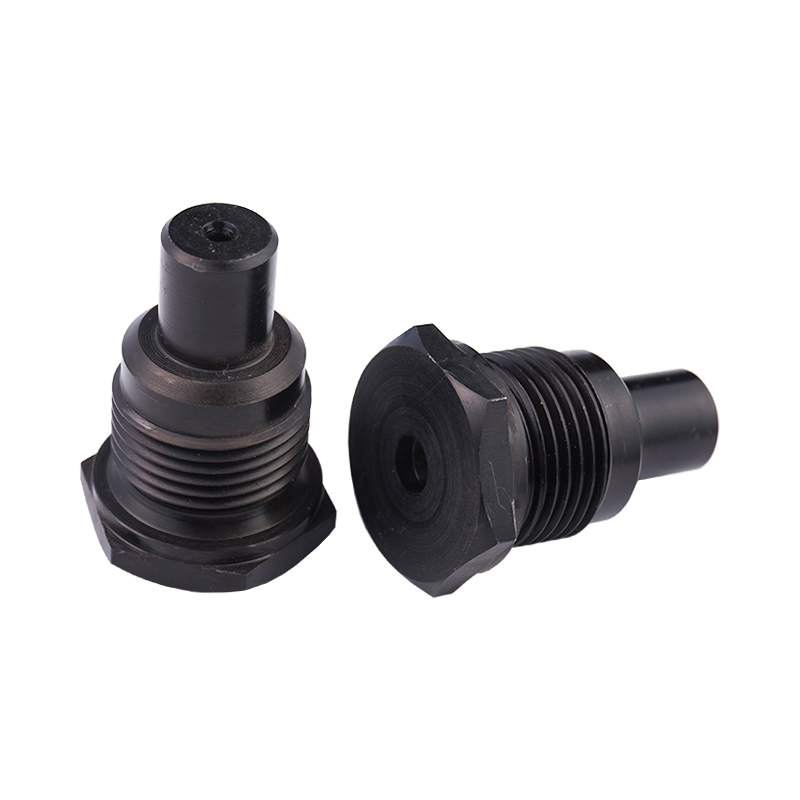
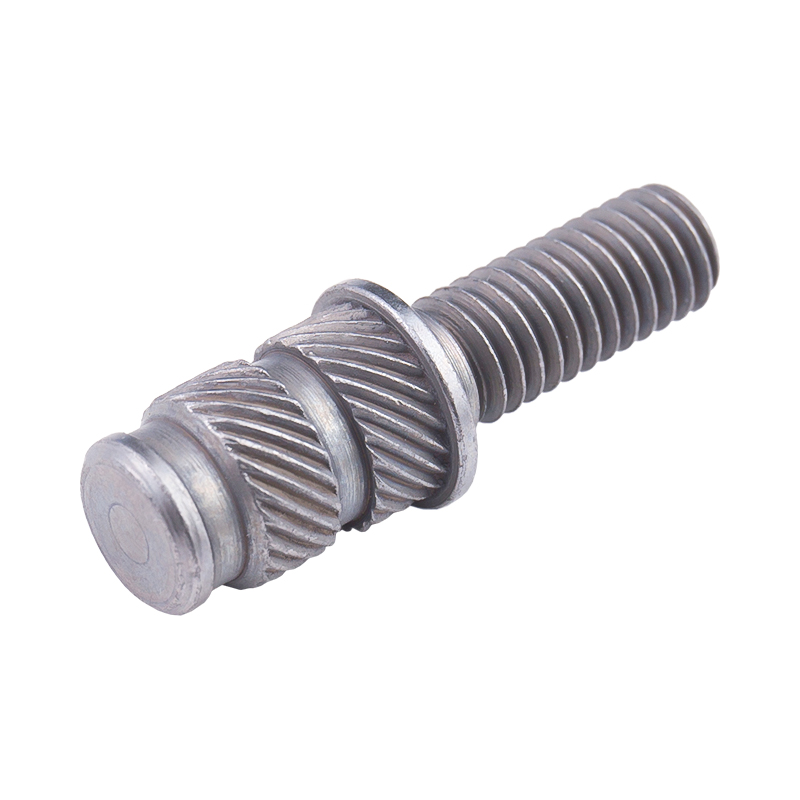
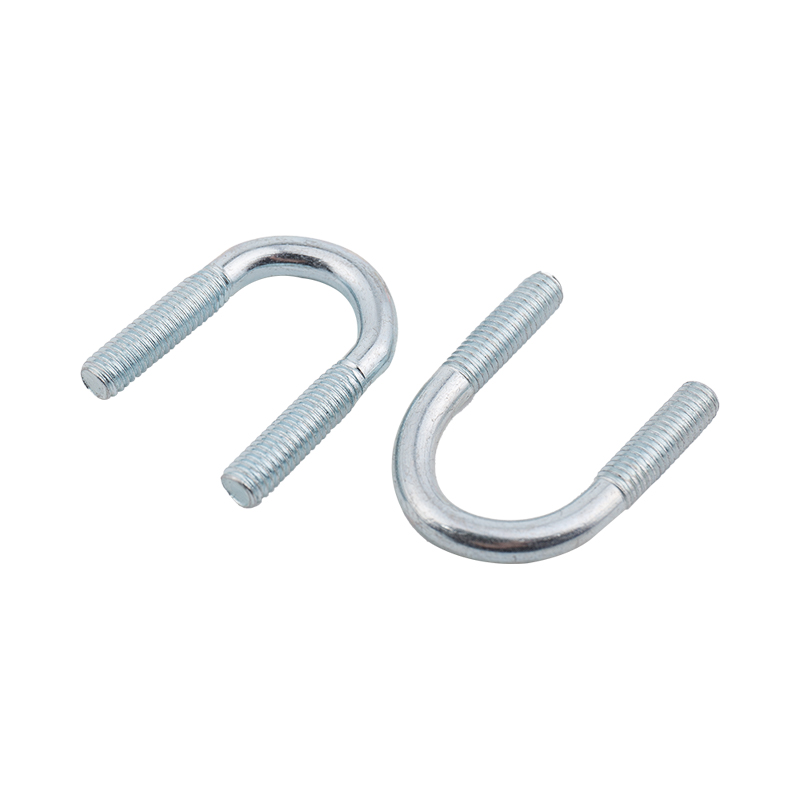
Definition and Basic Concept of Hexagonal Rivet Nuts Hexagonal rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to create strong, load-bearing threads in thin or hollow materials where convention...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Understanding Sealing Requirements in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Hydraulic and pneumatic connections operate under internal pressure, media flow, and frequent pressure fluctuations. In these syst...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Screw Hardware Screw hardware is a fundamental component in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. It plays a critical role in joining materials securely, providing structural ...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Round Head Cross Bolts Round head cross bolts are a type of fastener widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. They feature a rounded head with a cross slot ...
READ MORE
How do material modifications affect the mechanical properties of non-standard carbon steel bolts?
Material modifications can have a significant impact on the mechanical properties of non-standard carbon steel bolts. Here's how different modifications can affect these properties:
Alloying Elements: Introducing alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, nickel, chromium, or molybdenum can alter the mechanical properties of carbon steel bolts. For example, adding chromium can increase corrosion resistance, while molybdenum can enhance strength and hardness.
Carbon Content: Adjusting the carbon content of the steel can affect its hardness, strength, and ductility. Higher carbon content generally results in increased hardness and strength but decreased ductility. Conversely, lower carbon content can improve ductility but may reduce hardness and strength.
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering can significantly influence the mechanical properties of carbon steel bolts. Quenching involves rapid cooling to harden the steel, increasing its strength and hardness. Tempering then reduces the brittleness caused by quenching while maintaining sufficient strength.
Cold Working: Cold working, such as cold forging or cold drawing, can increase the strength and hardness of carbon steel bolts by inducing plastic deformation without altering the chemical composition. This process can also improve the bolt's surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Grain Size: Modifying the grain size through processes like grain refinement or controlled rolling can affect the mechanical properties of carbon steel bolts. Finer grains generally lead to increased strength and toughness due to grain boundary strengthening mechanisms.
Surface Treatment: Surface treatments like galvanization or coating can enhance the mechanical properties of carbon steel bolts by providing additional protection against corrosion, wear, and fatigue. These treatments can also improve surface hardness and reduce friction, thereby increasing the bolt's durability and performance.
What are the common challenges encountered during the production of non-standard carbon steel bolts, and how are they addressed?
Material Selection: Choosing the right grade of carbon steel with suitable mechanical properties and alloying elements can be challenging. It requires thorough knowledge of material specifications and application requirements.
Customization Complexity: Non-standard carbon steel bolts often require complex customization in terms of dimensions, structure, and surface treatment. This complexity can pose challenges in manufacturing, especially for mass production. To address this, manufacturers invest in advanced machining and fabrication technologies that can accurately produce customized bolts according to precise specifications.
Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality across batches of non-standard bolts can be challenging due to the variations introduced by customization processes. Quality control measures such as in-process inspections, dimensional checks, and material testing are essential to identify defects early in the production process. Additionally, implementing stringent quality management systems helps maintain high standards throughout manufacturing.
Surface Treatment Uniformity: Achieving uniform surface treatment, such as galvanization or coating, on non-standard carbon steel bolts can be challenging, particularly for intricate designs or large batches. Manufacturers employ advanced surface treatment techniques, including automated coating systems and controlled dipping processes, to ensure uniform coverage and thickness of surface treatments.
Dimensional Accuracy: Maintaining tight tolerances and dimensional accuracy in non-standard carbon steel bolts is crucial to ensure proper fit and functionality in assembly. Precision machining equipment, computer-aided design (CAD), and computer numerical control (CNC) machining are utilized to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. Regular calibration and maintenance of machining equipment are essential to uphold accuracy.



 русский
русский Español
Español