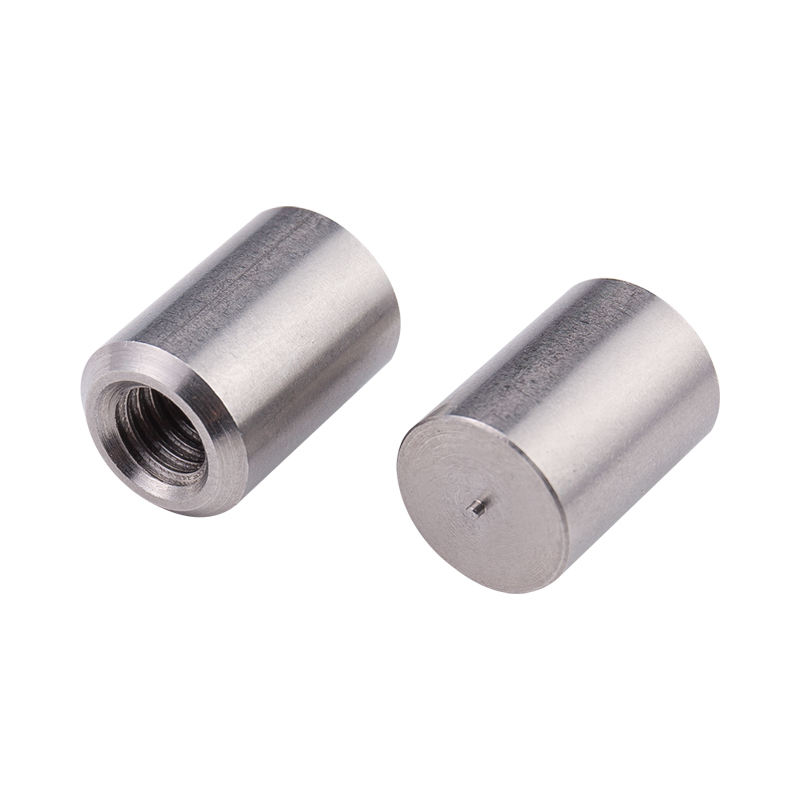
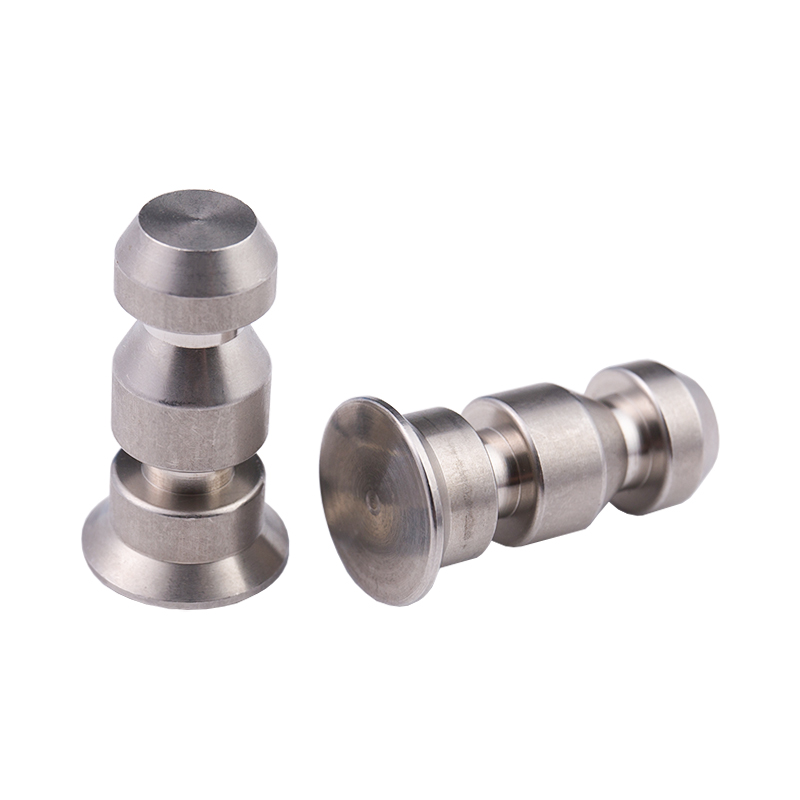
Definition and Basic Concept of Hexagonal Rivet Nuts Hexagonal rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to create strong, load-bearing threads in thin or hollow materials where convention...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Understanding Sealing Requirements in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Hydraulic and pneumatic connections operate under internal pressure, media flow, and frequent pressure fluctuations. In these syst...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Screw Hardware Screw hardware is a fundamental component in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. It plays a critical role in joining materials securely, providing structural ...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Round Head Cross Bolts Round head cross bolts are a type of fastener widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. They feature a rounded head with a cross slot ...
READ MORE
Can non-standard stainless steel welding nails be easily removed or replaced if necessary?
Welding Method: If the non-standard stainless steel welding nails are attached using techniques such as arc welding or resistance welding, they may be more challenging to remove compared to other methods like adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening.
Material Compatibility: The material the non-standard stainless steel welding nails are attached to can affect their removability. For example, if they are welded to a thick metal substrate, removing them may require significant effort, potentially involving grinding or cutting.
Head Design: Some non-standard stainless steel welding nails may have features designed to facilitate removal, such as a threaded or grooved head that allows for easier gripping with tools. However, this depends on the specific customization requested for the nails.
Accessibility: The accessibility of the nails can impact how easily they can be removed or replaced. Nails located in hard-to-reach areas or those surrounded by other components may require additional effort or specialized tools for extraction.
Damage to Substrate: Removing non-standard stainless steel welding nails may result in damage to the substrate, especially if they are welded directly onto the surface. Careful consideration should be given to the potential consequences of removal, such as surface marring or distortion.
While non-standard stainless steel welding nails can offer durability and strength, their ease of removal or replacement may vary depending on multiple factors.
Can non-standard stainless steel welding nails be used in conjunction with other fastening methods or materials?
Hybrid Fastening Systems: non-standard stainless steel welding nails can be used alongside other fasteners such as bolts, screws, or adhesives to create a hybrid fastening system. This approach allows for distributing loads more evenly and enhancing overall structural integrity.
Secondary Fastening: In applications where welding nails alone may not provide sufficient holding strength, supplementary fasteners like screws or bolts can be used in conjunction with welding nails to reinforce connections, especially in high-stress areas.
Complementary Materials: Depending on the substrate and the specific requirements of the application, combining welding nails with materials like epoxy adhesives, sealants, or mechanical anchors can enhance bonding strength, provide corrosion protection, or improve sealing against environmental elements.
Temporary Fixturing: Welding nails can be used temporarily to hold components in place during fabrication or assembly processes. Once the assembly is complete, permanent fasteners or bonding methods can be employed to secure the components together.
Multi-Material Joining: In cases where joining different materials is necessary, welding nails can be used in conjunction with techniques like riveting, clinching, or adhesive bonding to create robust joints that leverage the strengths of each material involved.



 русский
русский Español
Español