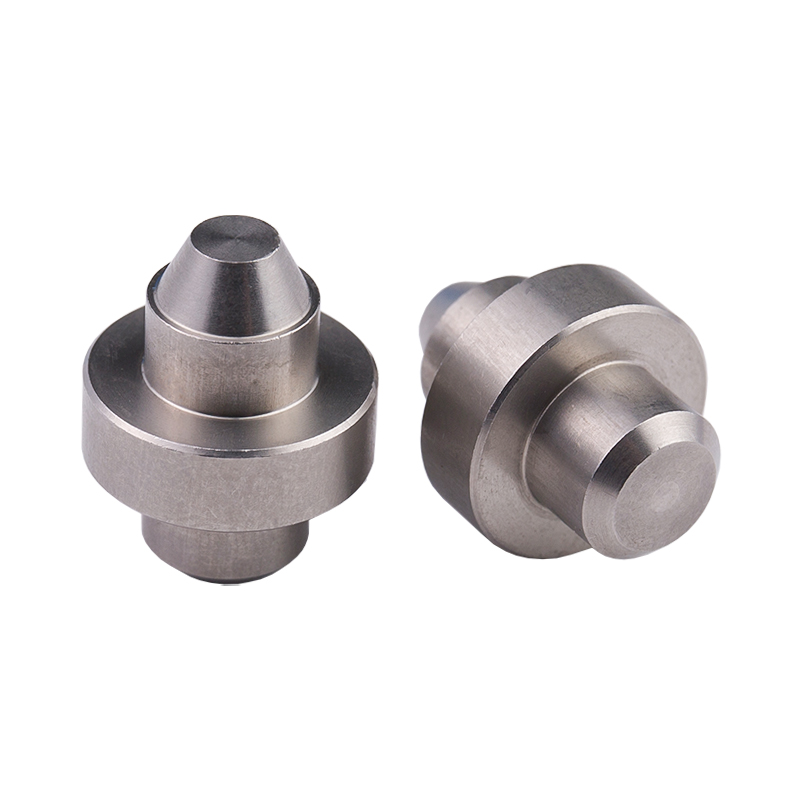
Definition and Basic Concept of Hexagonal Rivet Nuts Hexagonal rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to create strong, load-bearing threads in thin or hollow materials where convention...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Understanding Sealing Requirements in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Hydraulic and pneumatic connections operate under internal pressure, media flow, and frequent pressure fluctuations. In these syst...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Screw Hardware Screw hardware is a fundamental component in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. It plays a critical role in joining materials securely, providing structural ...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Round Head Cross Bolts Round head cross bolts are a type of fastener widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. They feature a rounded head with a cross slot ...
READ MORE
How do these studs contribute to the structural integrity in construction and manufacturing?
These studs are used to securely fasten various components together, such as beams, columns, and plates. By providing a strong connection, they enable the transfer of loads between structural elements, ensuring stability and strength in the overall structure.
In construction, welding studs are often employed to reinforce joints, particularly in critical areas where additional strength is needed. This reinforcement helps prevent failures due to bending, shear, or torsion, enhancing the structural integrity of the assembly.
Welding studs can enhance a structure's ability to withstand seismic forces by improving connections between elements. In earthquake-prone regions, properly installed studs help distribute forces more effectively, reducing the risk of structural damage or collapse during seismic events.
The high strength and toughness of non-standard welding studs make them capable of withstanding cyclic loading and fatigue, which are common challenges in dynamic structures like bridges and industrial equipment. By resisting fatigue, these studs help maintain structural integrity over the long term.
Non-standard carbon steel round welding studs can be customized according to specific project requirements, such as head shape, length, and diameter. This flexibility allows engineers to tailor connections to the demands of different applications, optimizing structural performance while minimizing material waste.
Carbon steel welding studs can be coated or treated to enhance their resistance to corrosion, especially in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or saltwater. By mitigating corrosion, these studs maintain their strength and integrity over time, prolonging the lifespan of structures.
Welding studs offer a fast and efficient method of assembly compared to traditional bolting or riveting techniques. Their quick installation reduces construction time and labor costs while ensuring reliable connections, contributing to overall project efficiency.
What is the composition of non-standard carbon steel round welding studs?
The composition of non-standard carbon steel round welding studs typically consists of primarily carbon steel alloyed with small amounts of other elements to achieve specific mechanical properties and welding characteristics. The exact composition can vary depending on the desired strength, toughness, weldability, and corrosion resistance required for the application.
Carbon (C): Carbon is the main alloying element in carbon steel, contributing to its strength and hardness. Higher carbon content generally increases strength but may reduce weldability and toughness if not properly controlled.
Manganese (Mn): Manganese is often added to improve the strength, hardenability, and weldability of carbon steel. It also helps remove impurities and enhance the steel's cleanability during manufacturing.
Silicon (Si): Silicon improves the steel's strength and hardness and helps deoxidize the molten weld pool during welding, reducing the formation of defects like porosity.
Sulfur (S) and Phosphorus (P): These elements are typically considered impurities in steel and are kept as low as possible to maintain good weldability and mechanical properties. Higher levels of sulfur and phosphorus can lead to brittleness and reduced toughness.



 русский
русский Español
Español