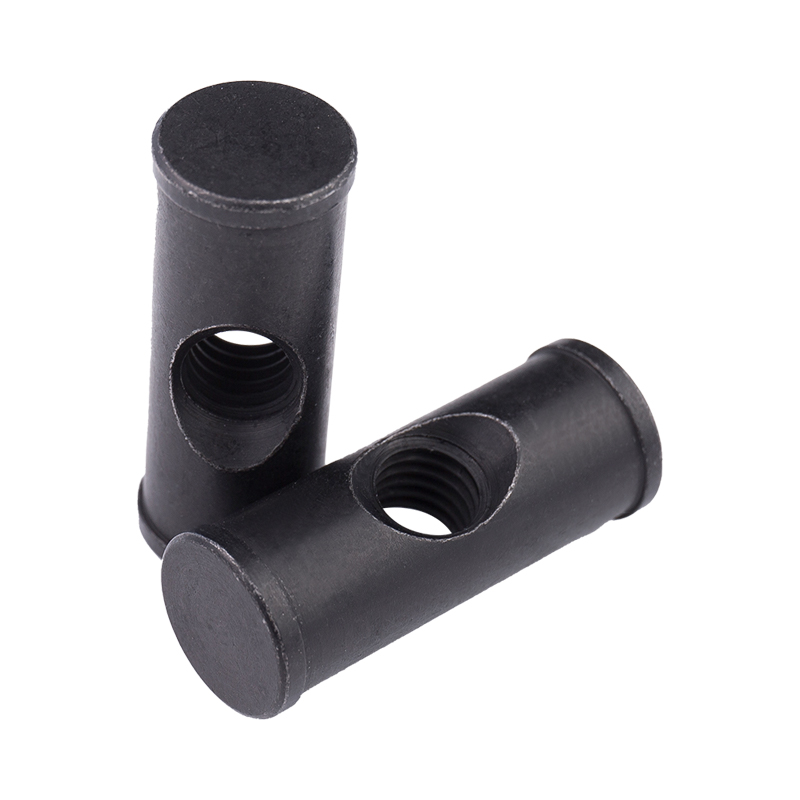
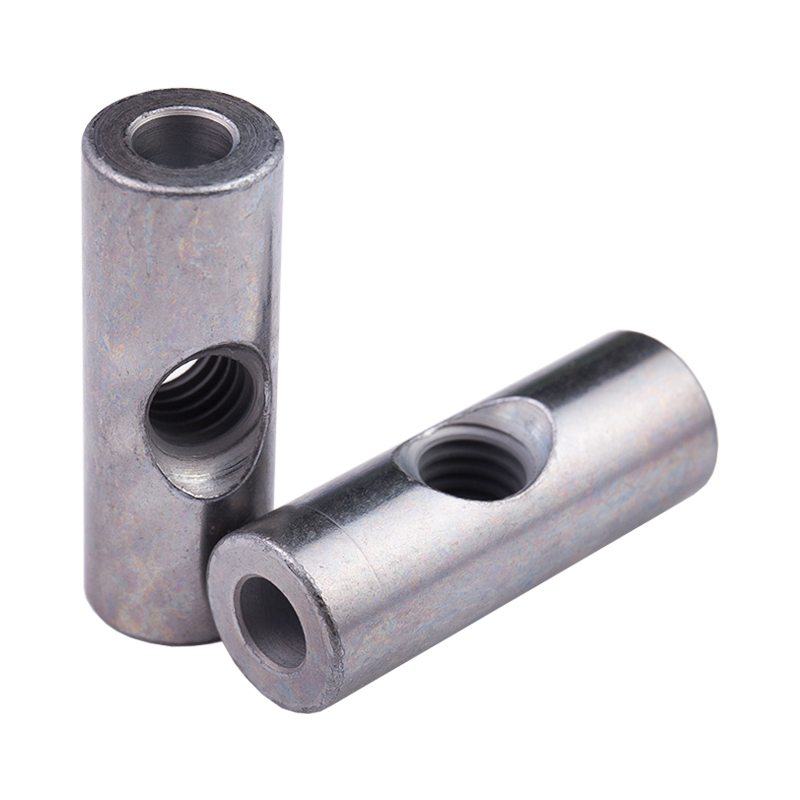
Definition and Basic Concept of Hexagonal Rivet Nuts Hexagonal rivet nuts are internally threaded fasteners designed to create strong, load-bearing threads in thin or hollow materials where convention...
READ MOREThe company has obtained two quality system management certificates of ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016.
At present, the company has been for Japan, Sweden, the United States, Singapore, Malaysia, Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta and many other customers to provide services, now the main customers are: Japan Sharp (SHARP), Japan SMC, Japan Panasonic (Panasonic), the Swedish automobile VOVOL, etc., all the fixed assets investment of more than 30 million dollars, welcome friends from all walks of life to the factory to visit, study, consulting and come! We welcome friends from all walks of life to visit our factory, investigate, consult and come to us for sample processing.
We are looking forward to establishing a good business partnership with you with mutual trust and reciprocity!
-
-
Understanding Sealing Requirements in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems Hydraulic and pneumatic connections operate under internal pressure, media flow, and frequent pressure fluctuations. In these syst...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Screw Hardware Screw hardware is a fundamental component in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects. It plays a critical role in joining materials securely, providing structural ...
READ MORE -
Introduction to Round Head Cross Bolts Round head cross bolts are a type of fastener widely used in construction, machinery, and industrial applications. They feature a rounded head with a cross slot ...
READ MORE
What are the tensile and yield strengths of the automotive carbon steel movable core?
The tensile and yield strengths of automotive carbon steel movable cores can vary depending on the specific grade of carbon steel used and any additional treatments applied. However, general ranges for common carbon steel grades used in automotive applications can provide a useful reference. Here are typical values for some standard grades of carbon steel:
Common Carbon Steel Grades and Their Properties
AISI 1045 (Medium Carbon Steel):
Tensile Strength: Approximately 570-700 MPa (83,000-101,500 psi)
Yield Strength: Approximately 300-400 MPa (43,500-58,000 psi)
AISI 1018 (Low Carbon Steel):
Tensile Strength: Approximately 440-550 MPa (64,000-80,000 psi)
Yield Strength: Approximately 370-400 MPa (54,000-58,000 psi)
AISI 1020 (Low Carbon Steel):
Tensile Strength: Approximately 410-520 MPa (60,000-75,000 psi)
Yield Strength: Approximately 210-350 MPa (30,000-51,000 psi)
AISI 1060 (High Carbon Steel):
Tensile Strength: Approximately 840-960 MPa (122,000-139,000 psi)
Yield Strength: Approximately 680-790 MPa (99,000-115,000 psi)
Factors Affecting Strength
Heat Treatment: Processes like quenching and tempering can significantly alter the tensile and yield strengths.
Cold Working: Work hardening through processes like rolling or drawing can increase strength.
Alloying Elements: Addition of elements such as manganese, chromium, and vanadium can improve strength and other mechanical properties.
To determine the exact tensile and yield strengths of a particular automotive carbon steel movable core, it would be necessary to know the precise material specifications, including the grade and any treatments applied. Manufacturers often tailor the material properties to meet specific performance requirements of the application.
If you need detailed specifications for a particular product, it would be best to consult the technical datasheet provided by the manufacturer or supplier of the movable core. This datasheet would include precise mechanical properties and any relevant testing standards or conditions under which the properties were measured.



 русский
русский Español
Español